- English
- Español
- Português
- русский
- Français
- 日本語
- Deutsch
- tiếng Việt
- Italiano
- Nederlands
- ภาษาไทย
- Polski
- 한국어
- Svenska
- magyar
- Malay
- বাংলা ভাষার
- Dansk
- Suomi
- हिन्दी
- Pilipino
- Türkçe
- Gaeilge
- العربية
- Indonesia
- Norsk
- تمل
- český
- ελληνικά
- український
- Javanese
- فارسی
- தமிழ்
- తెలుగు
- नेपाली
- Burmese
- български
- ລາວ
- Latine
- Қазақша
- Euskal
- Azərbaycan
- Slovenský jazyk
- Македонски
- Lietuvos
- Eesti Keel
- Română
- Slovenski
- मराठी
- Srpski језик
What is the difference between core and cavity?
2025-06-27
The core and cavity include the mold cavity and the mold core, which are tightly combined to form the overall shape and internal structure of the mold. The mold cavity is primarily responsible for forming the product’s internal shape and structure and controlling the product’s precision. Conversely, the mold core mainly forms the product’s external shape and structure, completing the overall molding of the product.
At this time, the mold core is tightly fitted to the cavity. When the molten plastic cools into a solid state, the core is pulled open, and the product on the core is ejected through the ejection system. Note, throughout this process, the cavity remains stationary, while the core moves.
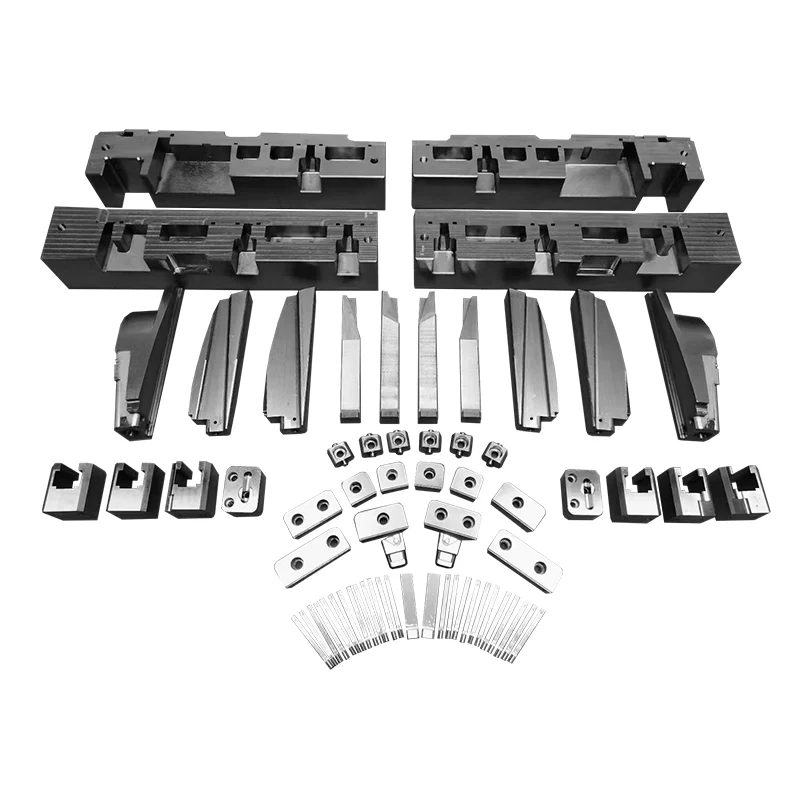

Differences Between The Core And Cavity
Besides the primary functions mentioned above, the differences between the cavity and core are reflected in the following aspects:
Procedural Differences During Injection
During the injection process, there are some differences in the procedural steps between the core and cavity. Plastic granules enter a closed space in the mold through a cavity (note that this closed space is formed by two parts, but most often, this space is considered part of the cavity, hence also referred to by many as the mold cavity).
Material Selection for Cavity and Core
Usage Cycle and Maintenance Variability
The usage cycle and maintenance of the core and cavity also differ. Since the cavity undergoes greater pressure and wear, its service life is usually shorter. Manufacturing companies often replace the cavity regularly to ensure product quality and production efficiency. In contrast, the core is subject to less wear and pressure, so its service life is relatively longer.
There are also some differences in material selection for the core and cavity. Because the cavity has to withstand higher pressure and wear, it typically requires more wear-resistant materials, such as alloy steel or carbide. The core can use relatively softer materials, such as aluminum alloys, to better fill and cool during the product molding process.
Differential Pressure Endurance
Due to the differences in shape and function, the core and cavity withstand different pressures. The cavity usually has to withstand higher pressures because it needs to fully fill the mold cavity with the product material during the molding process and ensure the integrity of the product’s internal structure. The core withstands lower pressure, mainly to give the product a perfect appearance.