- English
- Español
- Português
- русский
- Français
- 日本語
- Deutsch
- tiếng Việt
- Italiano
- Nederlands
- ภาษาไทย
- Polski
- 한국어
- Svenska
- magyar
- Malay
- বাংলা ভাষার
- Dansk
- Suomi
- हिन्दी
- Pilipino
- Türkçe
- Gaeilge
- العربية
- Indonesia
- Norsk
- تمل
- český
- ελληνικά
- український
- Javanese
- فارسی
- தமிழ்
- తెలుగు
- नेपाली
- Burmese
- български
- ລາວ
- Latine
- Қазақша
- Euskal
- Azərbaycan
- Slovenský jazyk
- Македонски
- Lietuvos
- Eesti Keel
- Română
- Slovenski
- मराठी
- Srpski језик
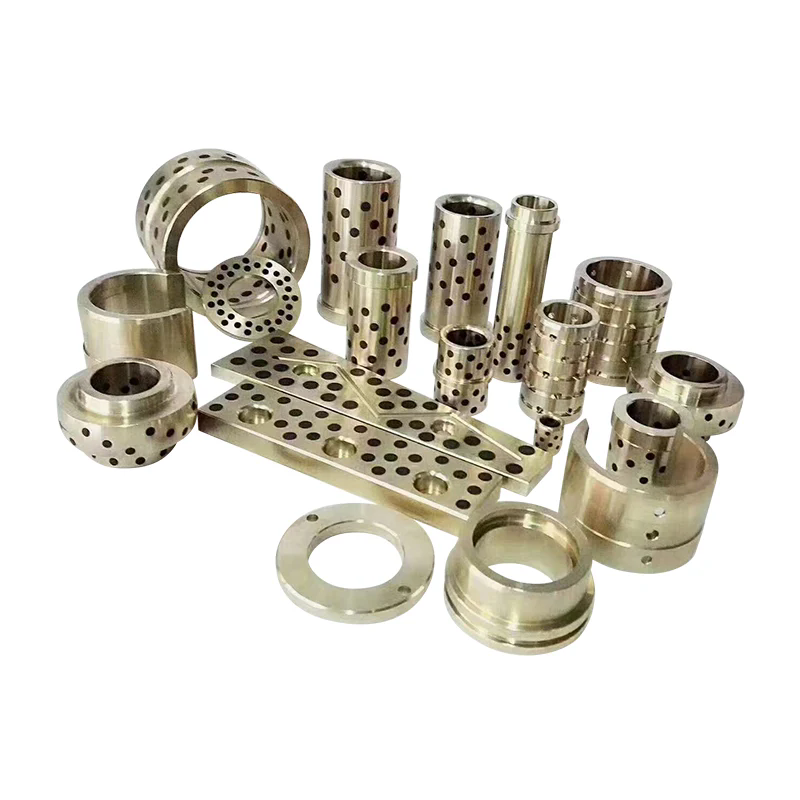
What Is the Function of Standard Part?
2025-09-12
In today’s global manufacturing ecosystem,has become central to engineers, procurement specialists, and business owners alike. Standard parts, also called general-purpose mechanical components, are those universally recognized, dimensionally consistent, and functionally reliable pieces used across industries to ensure compatibility, efficiency, and durability. These include items such as bolts, nuts, screws, washers, pins, bearings, seals, and fasteners that conform to international or national standards.
The primary function of a standard part is to provide uniformity and interchangeability. By following predefined standards, a bolt produced by one manufacturer can fit with a nut from another supplier without issue. This consistency eliminates costly customization, reduces downtime, and ensures supply chain flexibility. For industries such as automotive, aerospace, construction, and machinery manufacturing, the reliability of these parts directly determines product safety and performance.
Beyond mechanical performance, standard parts also play a role in cost reduction and process optimization. Since they are mass-produced at scale, manufacturers can benefit from lower production costs, reduced procurement lead times, and easier quality control. Moreover, they simplify product design since engineers can rely on existing specifications without reinventing every component.
The impact of standardization is evident across all industries. For example:
-
Automotive sector: bolts and fasteners following DIN/ISO standards guarantee that replacement parts can be sourced globally.
-
Aerospace industry: safety-critical fasteners meet stringent performance parameters to handle extreme temperature and pressure conditions.
-
Construction: anchors, nails, and screws standardized by size and strength make large-scale projects possible without compatibility issues.
In essence, the function of a standard part is not only mechanical support but also global compatibility, ensuring that industrial production runs smoothly regardless of supplier or geographic location.
Technical Features and Parameters of Standard Parts
When discussing the function of standard parts, it is critical to consider the technical specifications that define their performance. Standardization ensures that each parameter—whether mechanical strength, surface treatment, or dimensional tolerance—is globally recognized. Below is a professional summary of the most common technical parameters that customers and engineers evaluate:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Material | Carbon steel, stainless steel, alloy steel, brass, aluminum, plastics depending on application. |
| Strength Grade | Classified according to tensile strength (e.g., 4.8, 8.8, 10.9, 12.9 for bolts). |
| Surface Treatment | Zinc plating, hot-dip galvanizing, nickel plating, black oxide, anodizing, passivation. |
| Tolerance Class | Defines acceptable dimensional deviation (e.g., H7, g6, ISO fit standards). |
| Thread Standard | ISO metric, UNC/UNF, BSW, trapezoidal, fine-pitch threads. |
| Corrosion Resistance | Resistance to moisture, chemicals, and environmental stress tested in salt spray cycles. |
| Temperature Range | Operational capacity from -50°C to +500°C depending on material. |
| Certification | ISO 9001, CE, RoHS, REACH, ASTM, DIN, JIS approvals for global compliance. |
The selection of the right standard part depends on multiple considerations:
-
Load requirements – determining tensile, shear, or fatigue strength.
-
Environmental factors – exposure to humidity, salt, or chemical agents.
-
Industry-specific standards – aerospace demands different levels of precision compared to construction.
-
Lifecycle expectations – how long the part is expected to function without failure.
By integrating such parameters into procurement and design, companies reduce the risk of mismatch, improve durability, and enhance end-user satisfaction.
Why Standard Parts Are Indispensable for Industrial Growth
The real question is not only “What is the function of Standard Part?” but also “Why are they indispensable?” The answer lies in the long-term benefits they bring to industrial production, supply chains, and product lifecycle management.
a. Interchangeability and Efficiency
Without standardized bolts, nuts, and screws, every project would require custom-made solutions, inflating costs and timelines. Standardization ensures that engineers, regardless of country or company, can use compatible components immediately.
b. Global Trade and Sourcing
With standardized products, a manufacturer in Europe can confidently source parts from Asia or North America without concern over fitment issues. This global sourcing flexibility is essential in an era of interconnected supply chains.
c. Quality and Safety Assurance
Every standard part is manufactured under strict testing protocols. Whether tensile testing, hardness inspection, or torque testing, these parts undergo rigorous quality control before reaching the market. For industries such as medical equipment or aerospace, compliance with standards is not optional—it is mandatory for safety and certification.
d. Cost Savings and Scalability
Bulk manufacturing of standardized fasteners drastically reduces production costs. Additionally, when projects scale from prototypes to mass production, the same parts can be applied without modification, minimizing redesign.
e. Environmental and Sustainability Factors
Standard parts also contribute to sustainability. Since they are widely available, recycling systems for steel bolts, brass fittings, and aluminum fasteners are already in place, ensuring materials can be reused or reprocessed.
In practical terms, the function of standard parts extends beyond simple mechanical joining—they are the foundation of reliable, scalable, and sustainable industrial development.
Application Cases, FAQs, and Contact
To further clarify the role of standard parts, it helps to consider practical application cases:
-
Automotive Assembly Line: Thousands of fasteners ensure structural integrity. Standardization prevents assembly delays caused by incompatible parts.
-
Heavy Machinery: Large bolts and high-strength washers withstand vibration and fatigue in excavators and bulldozers.
-
Aerospace Engineering: Precision screws and rivets hold aircraft structures together under extreme stress conditions.
-
Electronics Manufacturing: Miniature screws and connectors provide reliable performance in high-density circuit boards.
FAQs About “What is the Function of Standard Part?”
Q1: What is the primary function of a standard part in machinery?
A1: The primary function is to provide secure, interchangeable, and reliable connections that comply with international standards, ensuring efficiency, safety, and compatibility across different suppliers and industries.
Q2: Why are standard parts more cost-effective than custom-made parts?
A2: Standard parts are mass-produced under regulated dimensions and quality grades, lowering unit cost. They reduce the need for custom tooling, shorten lead times, and allow businesses to source from multiple suppliers without compatibility concerns.
At Mudebao, we provide a comprehensive range of high-quality standard parts engineered to meet strict global requirements. Our commitment lies in delivering durability, precision, and certified reliability for industries worldwide.
If you are looking for trusted suppliers of standard parts for your projects, contact us today to discover how our expertise can help optimize your supply chain and manufacturing process.